Hits: 55 img
Aerogel is a lightweight solid material composed of nano-sized colloidal particles that form a nano-scale framework and nano-sized porous network structure, and which is filled with gaseous dispersed media in the pores. Due to its translucent color and extremely light weight, aerogel appears in the air like smoke, and is thus called "solid smoke".
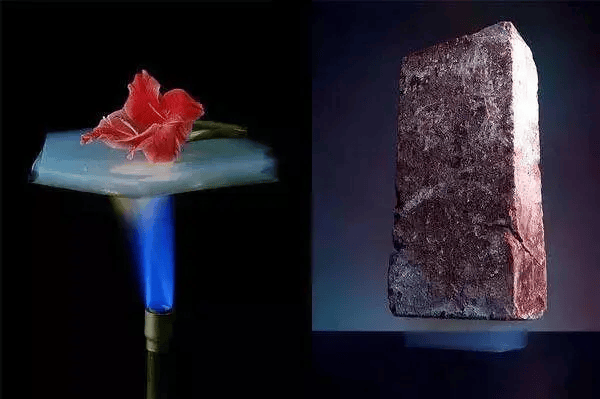
In 1931, American chemist Samuel Stephens Kistler prepared the world's first piece of aerogel. He dried the gel using supercritical technology (similar to jelly, consisting of a solid network framework and the liquid contained within the framework), replacing the liquid in the gel with air while maintaining the solid network structure of the gel from collapsing, thus obtaining aerogel. On the contrary, if the gel is dried directly, the capillary force caused by the evaporation of the liquid in the network usually causes the network to contract, resulting in a dense rather than porous material. This unique porous and loose structure gives aerogel characteristics such as extremely low density, extremely low thermal conductivity, and a large specific surface area. Due to these outstanding properties, aerogel is expected to be a "magical material that changes the world".
Join the Green Sharing Alliance for free
Aerogels possess extremely low density, ultra-high porosity, low thermal conductivity, and low acoustic impedance, which are characteristics not found in common solid materials. These properties give them significant application potential in areas such as heat insulation and preservation, biomedicine, sound insulation, and adsorption.
As the "thermal insulation king" in the field of materials, aerogel has extensive applications in aerospace, automotive batteries, construction, and other areas. The Russian "Peace" space station, the American "Mars Pathfinder" probe, China's "Long March Five" carrier rocket and "Zhu Rong" Mars rover have all used aerogel materials as insulation and heat preservation materials.
Aerogel is also used for heat insulation in ternary battery thermal runaway. Occasionally, situations occur where electric vehicle batteries catch fire. From the moment of ignition to the complete explosion of the entire vehicle often takes only a few seconds. The main reason is that the insulation level inside the battery is insufficient. The thermal runaway of a single cell expands to the entire battery pack. As a fireproof and heat insulation material, the most significant function of aerogel is to delay or prevent heat diffusion and the spread of flames. Its application in new energy vehicles can better achieve battery temperature control and electrical control management, improve performance, and play the roles of insulation and fire prevention, allowing users and passengers more time to escape the scene and extinguish the fire.
Furthermore, in low-temperature environments, the ability of electrons to move within the positive and negative electrode materials of lithium iron phosphate batteries deteriorates, resulting in capacity loss and reduced range. The excellent insulation properties of aerogels can prevent each cell within a lithium iron phosphate battery from being affected by external low temperatures.
In daily production and life, aerogels also have extensive applications: functional cellulose aerogels have inherent advantages in adsorbing gases such as carbon dioxide and formaldehyde, as well as removing heavy metal ions, organic dyes, organic solvents and oil wastewater from wastewater.
In the future, as the preparation process continues to improve and the technological level keeps advancing, aerogels will gradually become integrated into people's daily lives, bringing astonishing changes to various fields.